The most common infection that affects nearly 90% of people on earth is called HPV or human papillomavirus. Having discovered a papilloma, no one raises the alarm, because among people it is considered ordinary warts. Get rid of them only if they interfere or carry a cosmetic defect. The disease is "human" and is only transmitted from a patient to a healthy one: in everyday life, through touch, through the reproductive system, during childbirth from mother to baby. The disease can manifest itself on the skin or mucous membranes in the form of warts, papillomas or condyloma. Let's see what is HPV and how dangerous is it for humans?
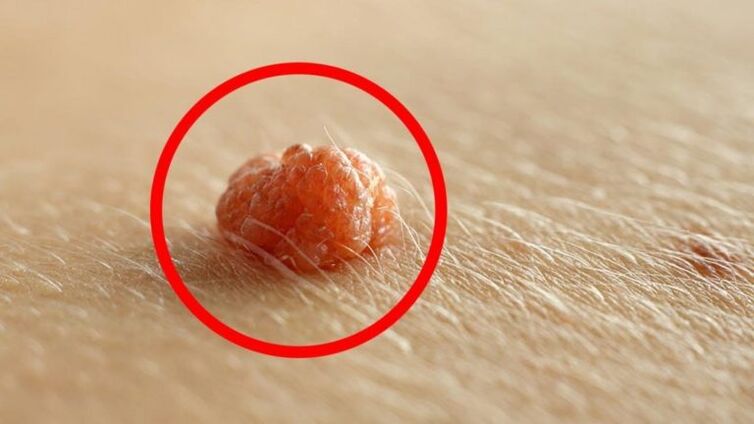
What is HPV?
The virus lives in almost every person. HPV germs are so small that they can enter the bloodstream through abrasions, scratches and small cuts on the skin. It may not show itself in any way throughout the wearer's lifetime, or it may constantly show itself in all its glory. The incubation period can range from a few weeks to several years. The action signal is the weakening of the immune system. If papillomas appear on the skin and mucous membranes, the body needs urgent treatment.
There are more than 70 types of human papillomaviruses, but several new strains are registered each year. Conventionally, all types of HPV infection can be divided into two groups.
Warts are viruses that cause the development of warts in the body.
- HPV types 1, 2, 3, 4 cause the formation of plantar warts or corns;
- HPV types 3, 10, 28, 49 are responsible for the appearance of flat warts;
- HPV type 27 forms "butcher's warts";
- HPV: 5, 7, 10, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19-24, 26, 27, 29, 57 - also develop warts.
Papilloma - viruses that cause the formation of papillomas and warts.
- HPV 6. 11, 13, 16, 18, 31, 33, 31, 33, 58, 52, 39, 70, 30, 40, 42, 43, 51, 55, 57, 59, 61, 62, 64, 67-69
What is the danger of HPV?
Why over the past few years have physicians sounded the alarm and tried to educate the public about HPV disease? Because the percentage of cancer patients who have been diagnosed with this virus is seriously increasing. Not only women with cancer of the uterus suffer from it, but also men with oncology of the male genitalia. The number of skin cancers in the elderly is also on the rise.
Of course, there are types of HPV that do not affect the internal health of a person, but their manifestations in the form of developed papillomas and warts are uncomfortable. They are classified as having low oncogenicity - minimal risk of developing cancer. Such formations are easily removed by folk methods or aesthetic medicine. But the virus itself is not treated by any means or medication. If a person is infected, they carry the virus all their life.
Other subspecies of papillomavirus infection belong to the group with high oncogenicity, that is, they can affect the formation of malignant neoplasms in the body.
There are 3 types of oncogenicity:
- Low cancer risk HPV: 6, 11, 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 70;
- Medium oncological risk HPV: 26, 31, 33, 35, 51, 52, 53, 58, 66;
- High-risk HPV: 16, 18, 36, 39, 45, 56, 59, 66, 68.
Diseases and types of HPV
Below we provide a list of papilloma virus types.
Skin lesions:
- Warts on the sole of the foot (corns) 1, 2, 4
- Common warts 2, 4, 26, 27, 29, 57
- Flat warts 3, 10, 28, 49
- warts butcher 7
- Epidermodysplasia veruciformis 2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19, 20-25, 36, 37, 46, 47, 50
Lesions of the mucous membranes of the genital organs:
- Genital warts 6, 11, 42-44, 54
- Epithelial lesions without invasion of other layers (intraepithelial lesions) may be precancerous 62, 64, 67-70
- Cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, anus and penis 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 54, 56, 66, 68
Non-genital mucosal lesions:
- Oral mucosal lesions (focal epithelial hyperplasia) 13, 32
- Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis 6, 11, 30
- Malignant tumors of head, neck, lungs 2, 6, 11, 16, 18, 30
Types of viral skin lesions
Most types of human papillomavirus infection are asymptomatic. The external manifestations of the disease are different, here are some types:
common warts
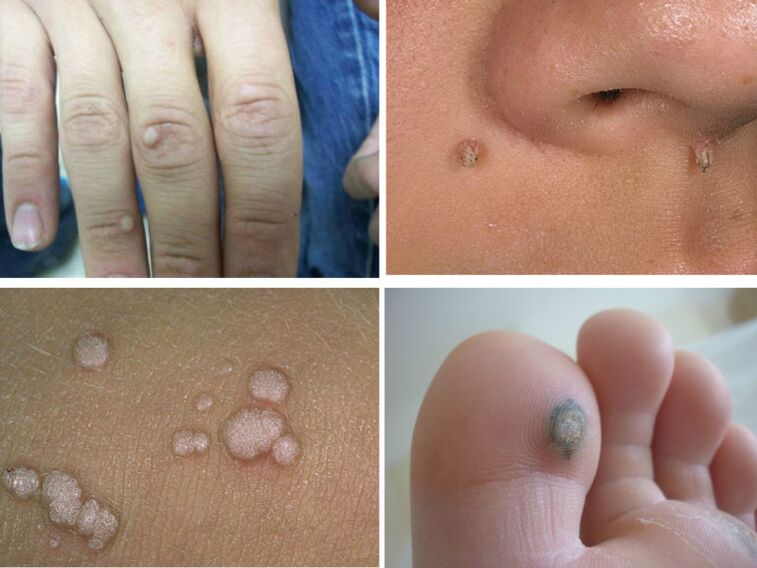
The most common form of HPV is the wart. Almost every person can find on his body a similar papule with a diameter of no more than 5-7 mm. Usually, warts are located on the outside of the palm, between the fingers, on the soles of the feet, on the chin, eyelids and scalp. Warts can enlarge and form colonies from the maternal papule. Then they can cause discomfort: itching and tingling in the places of growth.
The most "sick" are plantar warts, their common name is "thorns". When walking, they put pressure on the nerve endings, which causes severe pain. It is recommended to remove such growths surgically in clinics. Simple warts are not a threat to human health, they almost never turn into oncological tumors.
Butcher's Warts
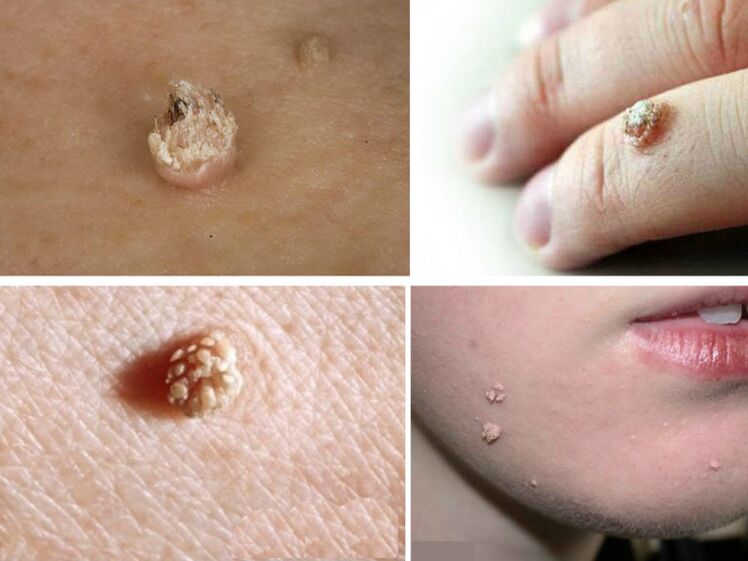
Butcher's warts look like several thick threads growing out of a single growth. Most commonly found on fingers, especially in places of cuts. Long filiform papules cause discomfort to their owner, since these formations are not aesthetic. They may bleed when hit or scratched. Although in the oncological sense, these warts are harmless, but their damage will lead to problems. The recommendation of doctors is to remove it without fail.
flat warts
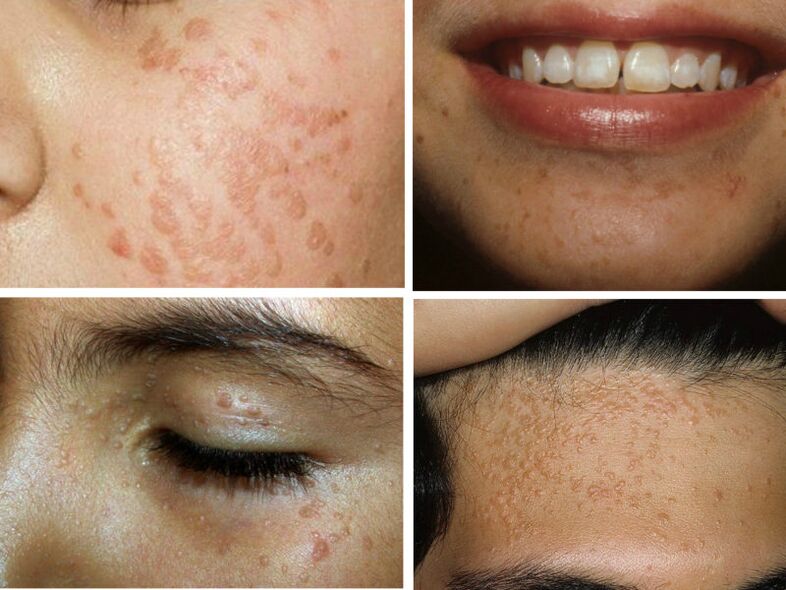
Flat warts are also called "adolescent warts" because they often appear during adolescence. They look like a large, clumped dry rash on the skin. Cover forehead, cheeks, chin, forearms. The color may not differ from the skin or be slightly darker.
Butcher's Warts
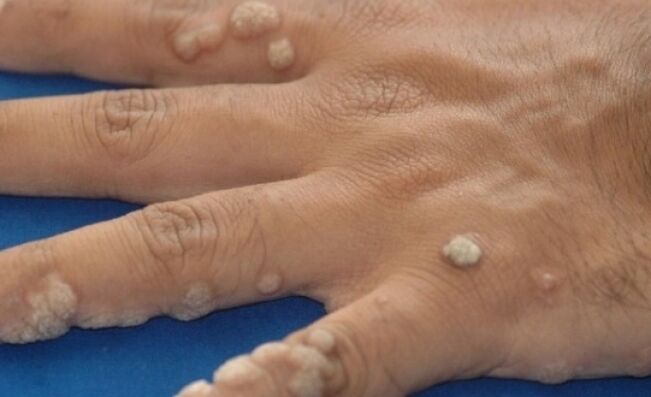
Butcher's warts are scarred, warty growths the color of normal skin. They can be both single and in clusters of several pieces. The name of these warts was given by the professional activities of butchers. It can be said that this type of infection is an occupational disease of the meat industry.
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis
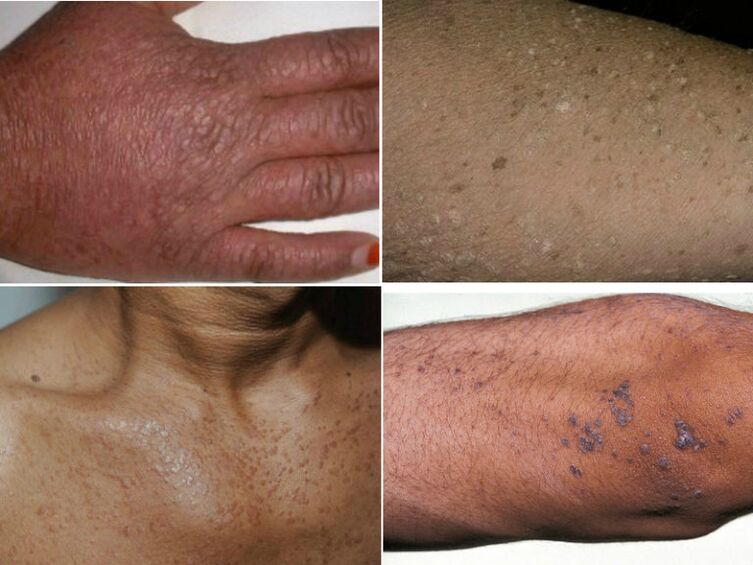
This disease can be confused with pityriasis versicolor, so you need to consult a specialist. It is transmitted hereditarily, but is very rare in the form of dermatosis. Outwardly, it looks like an accumulation of flat scaly rashes and age spots. The main localization sites are the face, neck and hands. Unfortunately, this form of wart can develop into cancer.
Periungual warts
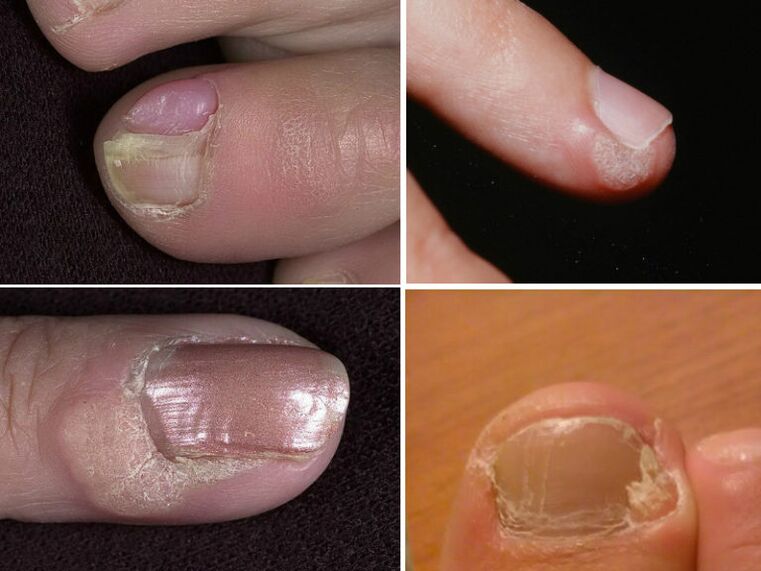
Warts located near the nail destroy the nail plate. They push deep into the skin and deform the finger. They do not develop into malignant formations, but that does not make them less undesirable. Surgery is necessary both for aesthetic reasons and for the health of the fingers.
Bowen's disease
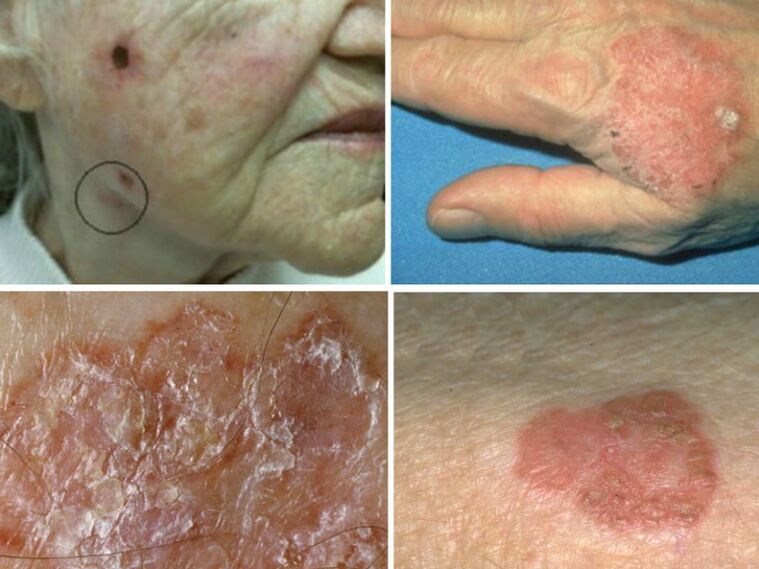
This form of HPV tends to degenerate into squamous cell carcinoma. When the skin is damaged, a redness of 5 mm is formed, which grows and becomes covered with crusts. The upper layer of the epidermis is affected, the growth can reach 5 cm in diameter. It is more common in the elderly, because the immune defenses are reduced.
Genital warts
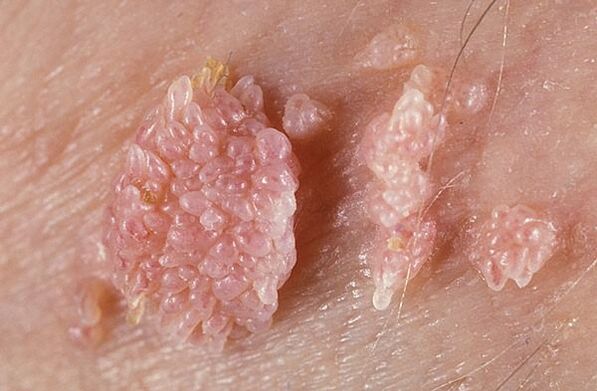
This type of HPV is sexually transmitted and therefore affects the genitals of both men and women, as well as the mucous membranes of the urinary system and anus. The appearance of the formations resembles a cauliflower or cockscomb. Genital warts can also appear in the corners of the mouth due to oral sex. Growths should be removed, since when rubbing it is possible to injure them and cause infection.
Papillomas of the oropharynx
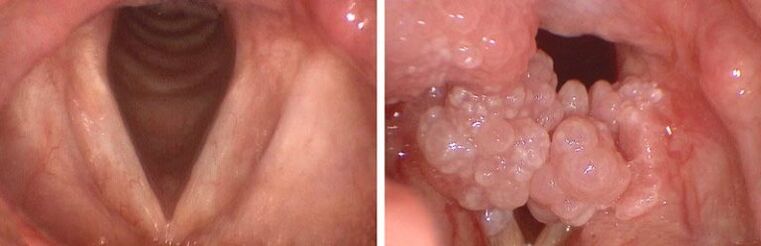
HPV infection in the mouth is also similar to cauliflower. White patches can travel down the lungs and trachea, making it difficult for a person to breathe. You can damage the papilloma by eating, which can lead to cancer. Since a malignant tumor cannot be distinguished from a benign tumor, it is necessary to do tests before removing the plaques.
Flowering papillomatosis can be not only in the elderly. The disease occurs in children and adults. The main signs of laryngeal papillomatosis are dysphonia (speech disorder) and aphonia (inability to speak), hoarseness and difficulty breathing.
Treatment methods
Methods for getting rid of papillomavirus infection do not exist today. Therefore, the treatment is reduced to the elimination of external formations and the suppression of the virus in the patient's body. There are cases when certain types of viruses died on their own in the body for several years. Which methods and preparations to use for treatment are determined by the doctor solely on the basis of diagnosis, tests and external examination of the patient.
Destructive methods:
- surgical excision (cutting) of the wart/papilloma (used only if a malignant lesion is suspected);
- electrocoagulation - cauterization of the formation with a coagulator through which an electric current passes;
- cryodestruction - the destruction of the wart with liquid nitrogen;
- laser processing - the impact on the formation of a laser beam;
- radio wave method - exposure to a wart / papilloma using the Surgitron device.
Chemical treatments:
- cauterization with salicylic acid;
- treatment of education trichloroacetic acid concentration of 50-90%;
- a mixture of acids - treatment with an educational preparation (the effectiveness is very low).
To activate the immune system and suppress HPV, drugs with antiviral and immunomodulatory effects should be included in therapy.
Disease prevention
It is quite difficult to avoid contracting the HPV virus, since it can be infected in a public bath, a swimming pool, when using common household items, in a hospital. But these strains are benign and do not cause cancer. Prevention usually comes down to personal hygiene, prompt treatment of cuts and wounds with antibacterial agents, and the use of protective equipment while working.
Particular attention should be paid to the prevention of the sexually transmitted virus. Protecting your body with condoms is unlikely to succeed. A viral infection in a partner can be near the genitals and in the mouth. The best way to avoid infection is pre-vaccination. Vaccinations should be given to both girls and boys before the onset of sexual activity at age 11-13. Immunity lasts 3-5-10 years and depends on the vaccine and the type of virus. Then the vaccination can be repeated if there is a risk of infection (change of sexual partner).
HPVs with a high oncogenic risk can in fact cause tissue modifications and lead to an oncological process. But several years pass between the first signs and the appearance of cancer. Therefore, it is so important to have annual medical checkups with a doctor, especially for women. Regular gynecological examination reveals changes in the external genitalia and cervix. Watch your health!























